Annotation of small proteins
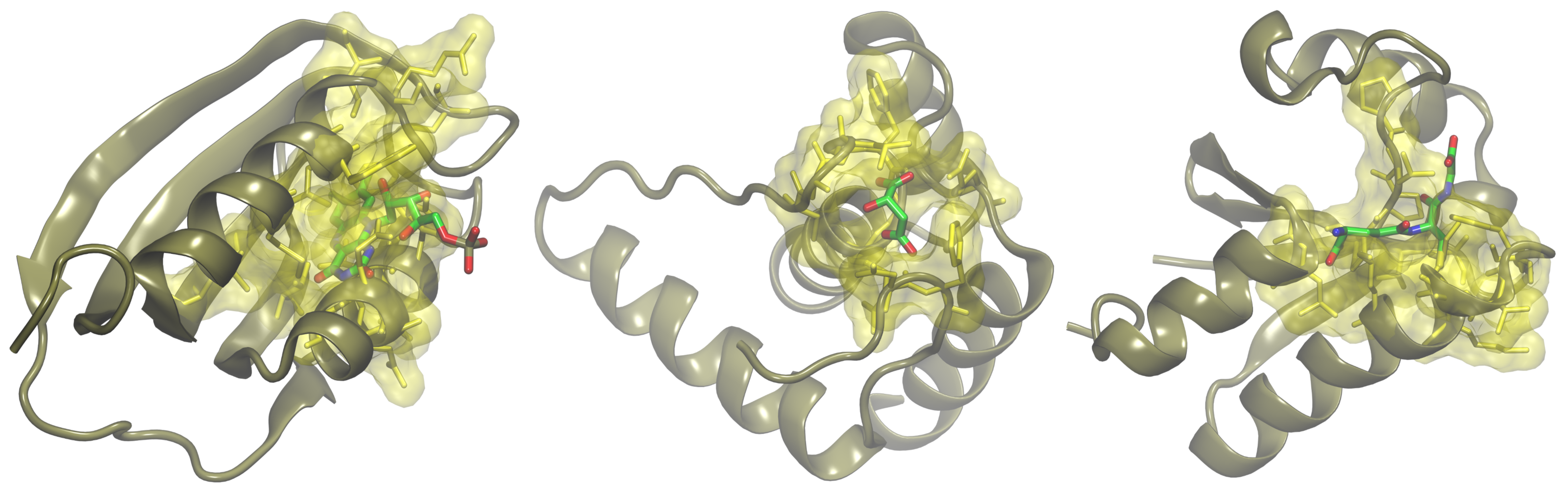
A growing body of evidence shows that gene products encoded by short open reading frames play key roles in numerous cellular processes. Yet, they are generally overlooked in genome assembly, escaping annotation because small protein-coding genes are difficult to predict computationally. There are still a considerable number of small proteins whose functions are yet to be characterized. To address this issue, we applied a collection of structural bioinformatics algorithms to infer molecular function of putative small proteins from the mouse proteome. Our results strongly indicate that many small proteins adopt three-dimensional structures and are fully functional, playing important roles in transcriptional regulation, cell signaling and metabolism.
