Drug repositioning for orphan diseases
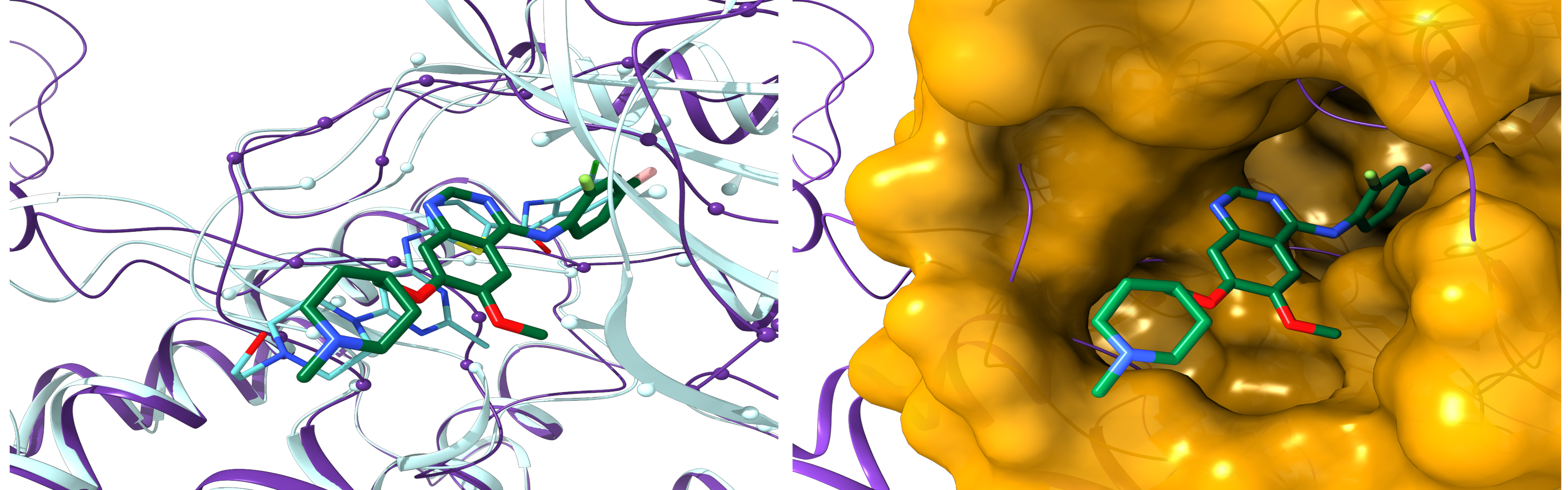
About 7,000 rare, or orphan, diseases affect more than 350 million people worldwide. Although these conditions collectively pose significant health care problems, drug companies seldom develop drugs for orphan diseases due to extremely limited individual markets. Computer-aided drug repositioning is a cheaper and faster alternative to traditional drug discovery offering a promising venue for orphan drug research. We developed eRepo-ORP, a comprehensive resource constructed by a large-scale repositioning of existing drugs to orphan diseases with eThread, eFindSite and eMatchSite. A systematic exploration of 320,856 possible links between known drugs in DrugBank and orphan proteins obtained from Orphanet revealed as many as 18,145 candidates for repurposing.
